Polylactic acid (PLA)

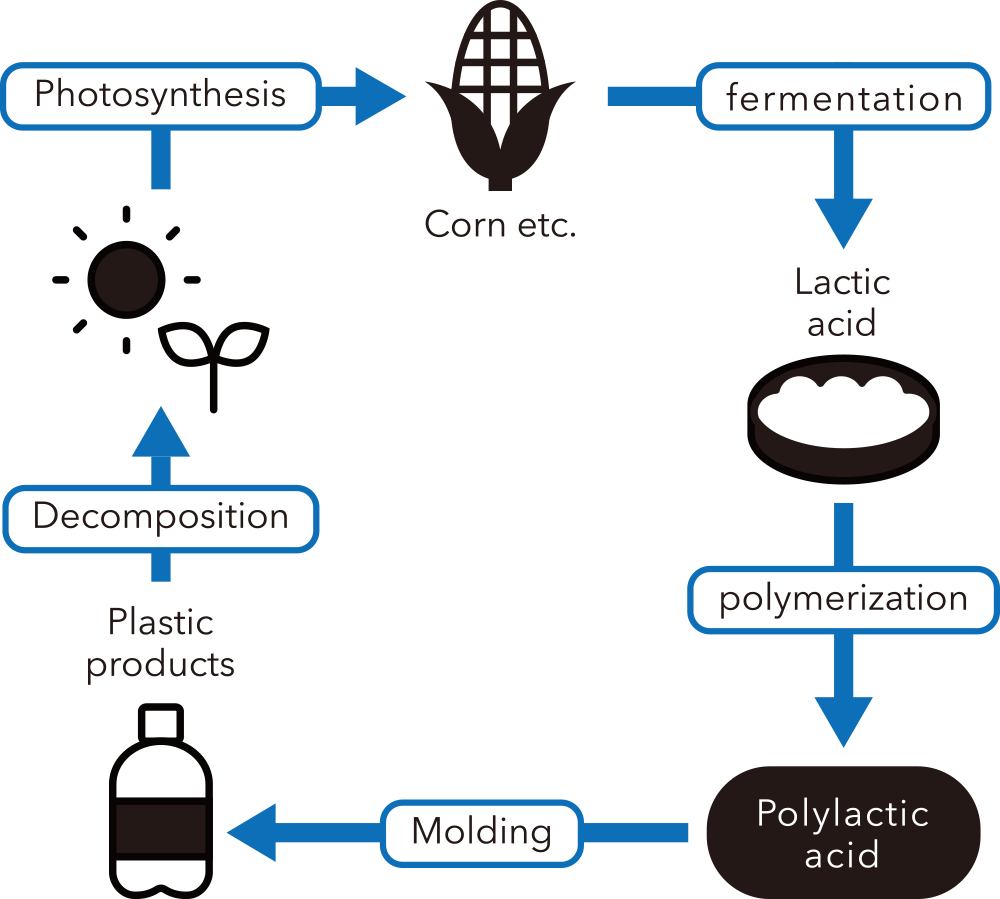
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a corn-based sustainable plastic.
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a plant-derived biodegradable plastic made from the starch contained in corn and other plants. Since it does not increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere when incinerated (carbon neutral), it has a lower impact on the environment than fossil-derived plastics. In addition, since it decomposes into water and carbon dioxide under certain environments (biodegradability), microplastics made from PLA will decompose in the natural environment and are thus expected to reduce environmental pollution.
Characteristics of polylactic acid (PLA)
| 1. Organics recycling | 2. Carbon Neutral | 3. Antibacterial properties |
|---|---|---|
| Polylactic acid (PLA) is a kind of plastic made from biomass raw materials such as corn. After being used, it decomposes into water and CO2 under certain conditions, returns to nature, and is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis, creating a cycle to produce corn and other plants. This is the perfect cyclical process that only biodegradable plastic can achieve. | Since polylactic acid (PLA) uses biomass such as corn as its raw material, it absorbs CO2 during the growth process of plants; therefore, even if incinerated, CO2 emissions into the atmosphere are essentially zero. | Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biocompatible and safe material made from lactic acid, which is also present in the human body. With antibacterial properties thanks to the action of lactic acid, PLA can exhibit an antibacterial effect even without using additives. |
Biodegradation of 100% polylactic acid (PLA) T-shirt
Compost temperature: 68°C (after 3 days, temperature at time of the T-shirt being taken out)
Moisture content: Around 50%
Experiment period: November 4th–10th, 2021
Conducted in cooperation with V&A Japan Corporation
Antibacterial properties
It has been confirmed that 40% polylactic acid (PLA)/cotton blended fabric maintains an excellent antibacterial effect even after it has been washed 10 times after fibrillization.
It was recognized to exhibit an antibacterial effect with an antibacterial activity value of 2.2 or more.
*Quoted from JIS 1902: 2015/Table F.1
| Antibacterial activity value: Before washing | Antibacterial activity value: After washing 10 times |
|---|---|
Partner company

Certifications acquired
Japan Bioplastics Association (JBPA)

Polylactic acid resin
FY200, 400, 600, and 800 series
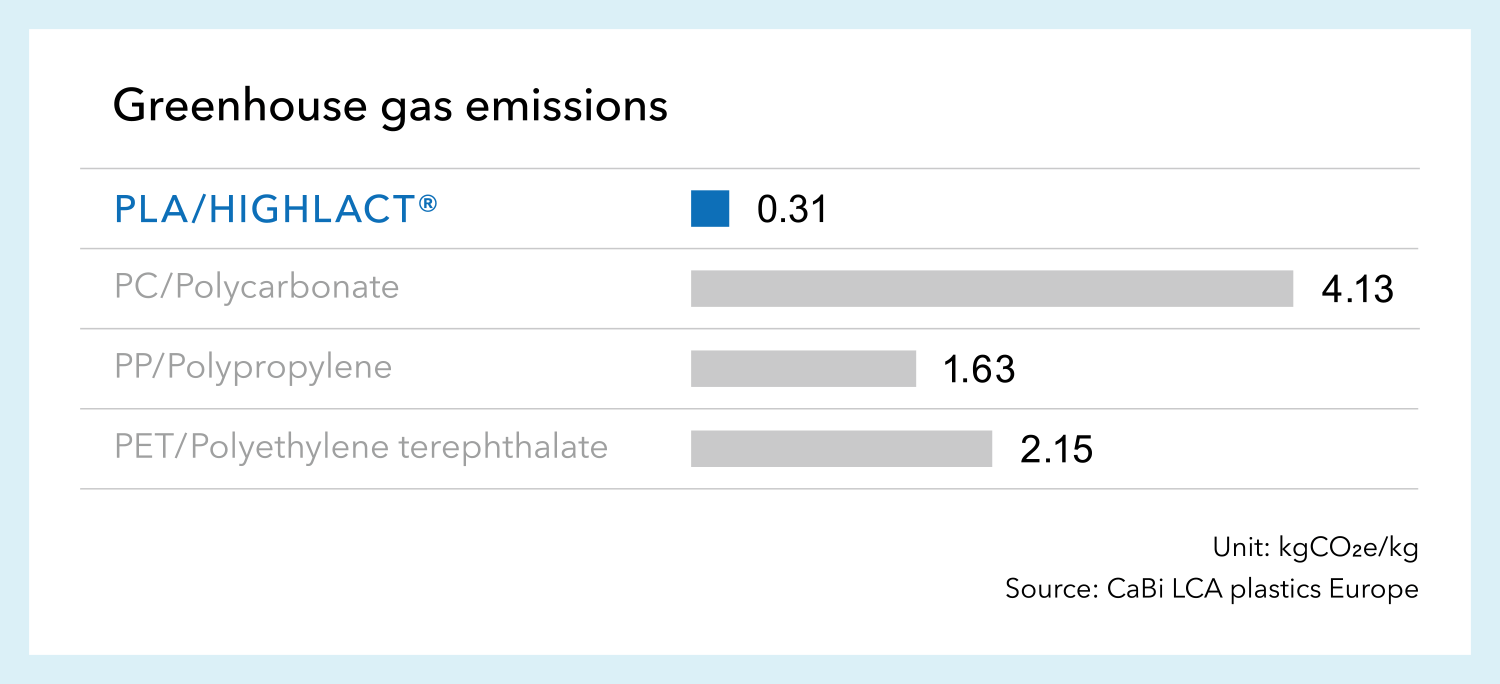
LCA (life cycle assessment) of polylactic acid (PLA)
Acquired certification based on ISO 14040 and ISO 14044.
LCA Certificate ▶ View PDF file
Polylactic acid (PLA) resin Table of main grade physical properties

Applications of polylactic acid (PLA)
線維・不織布用途
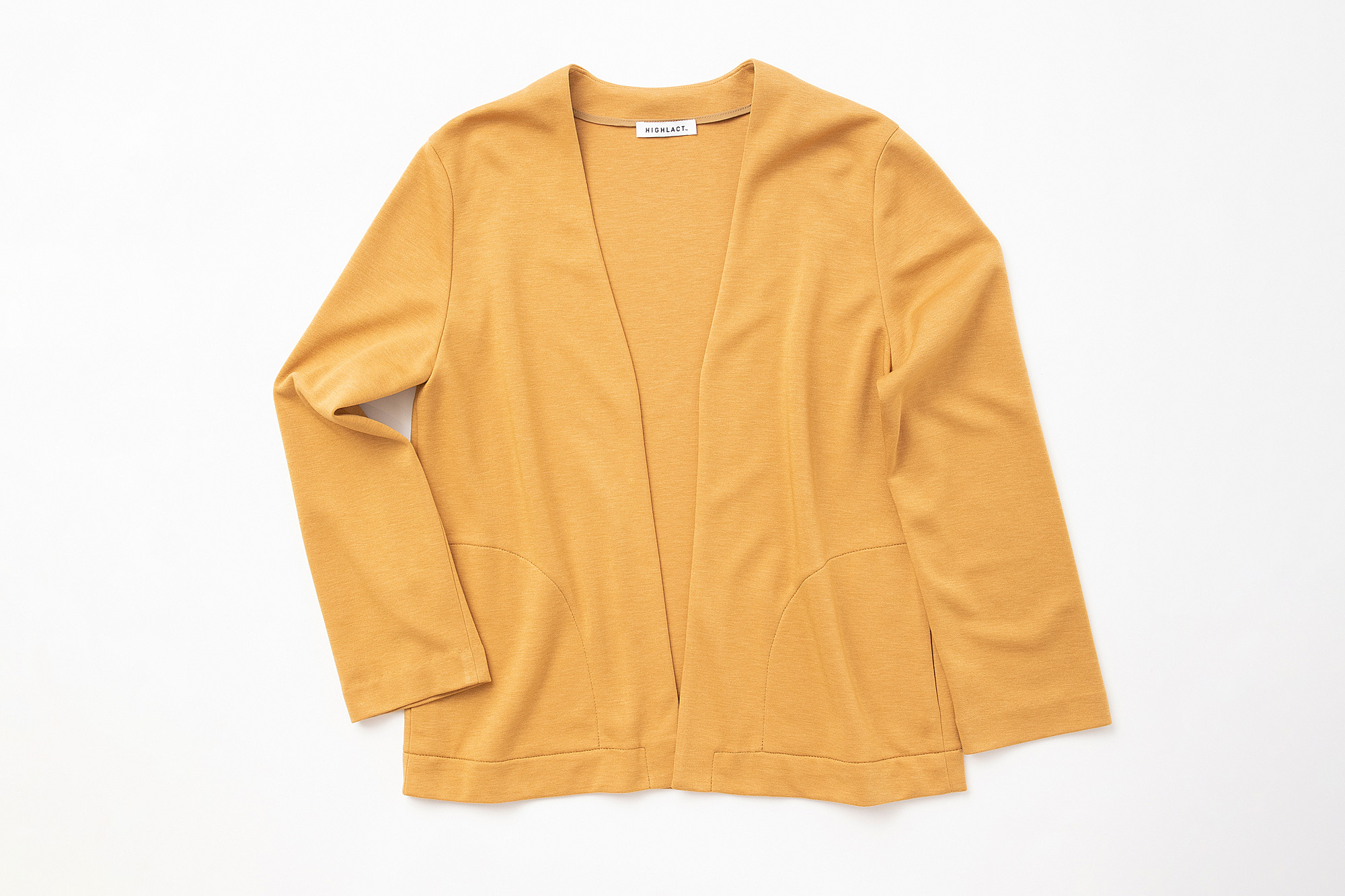
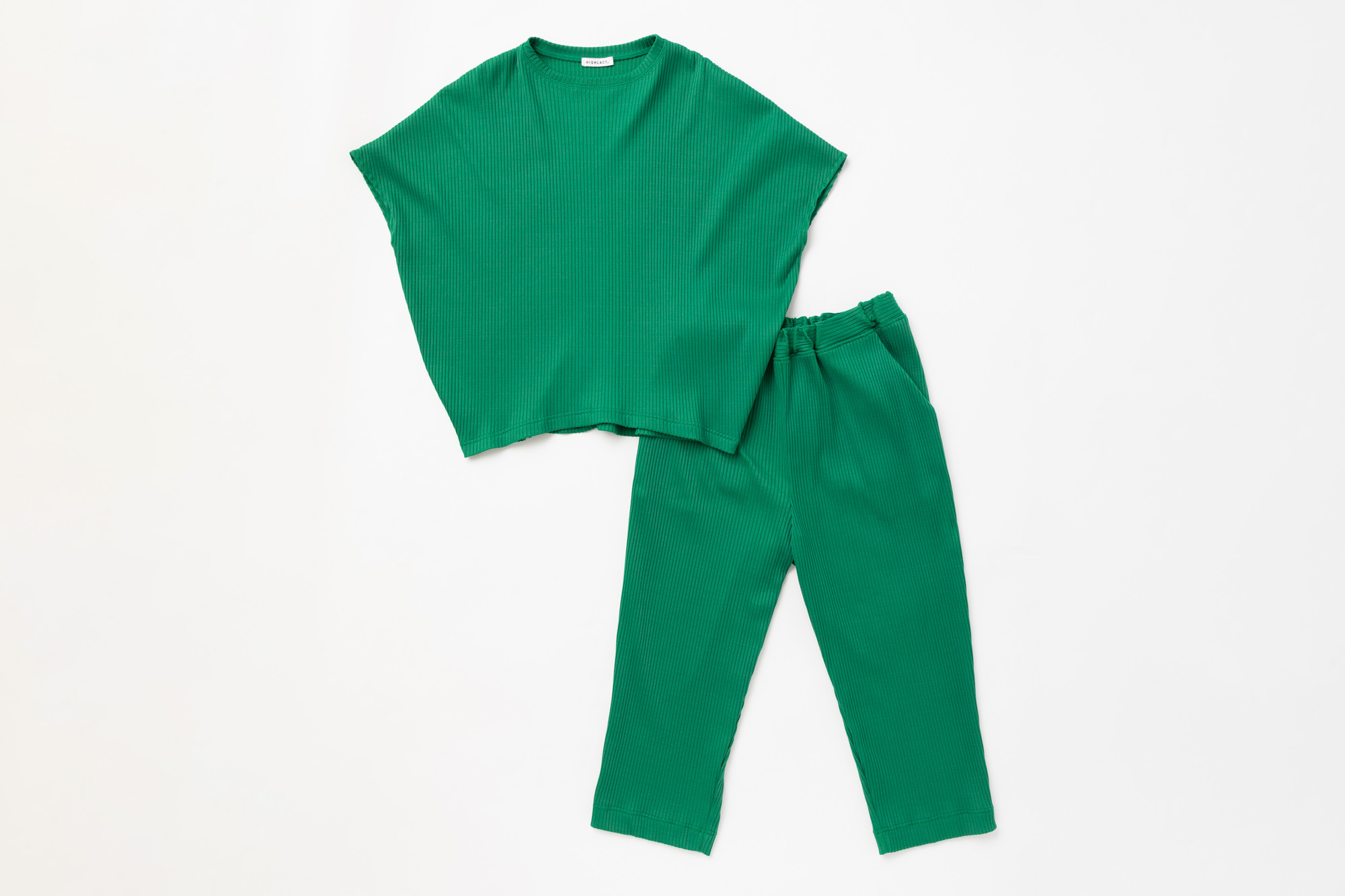
Used for fibers and non-woven fabrics
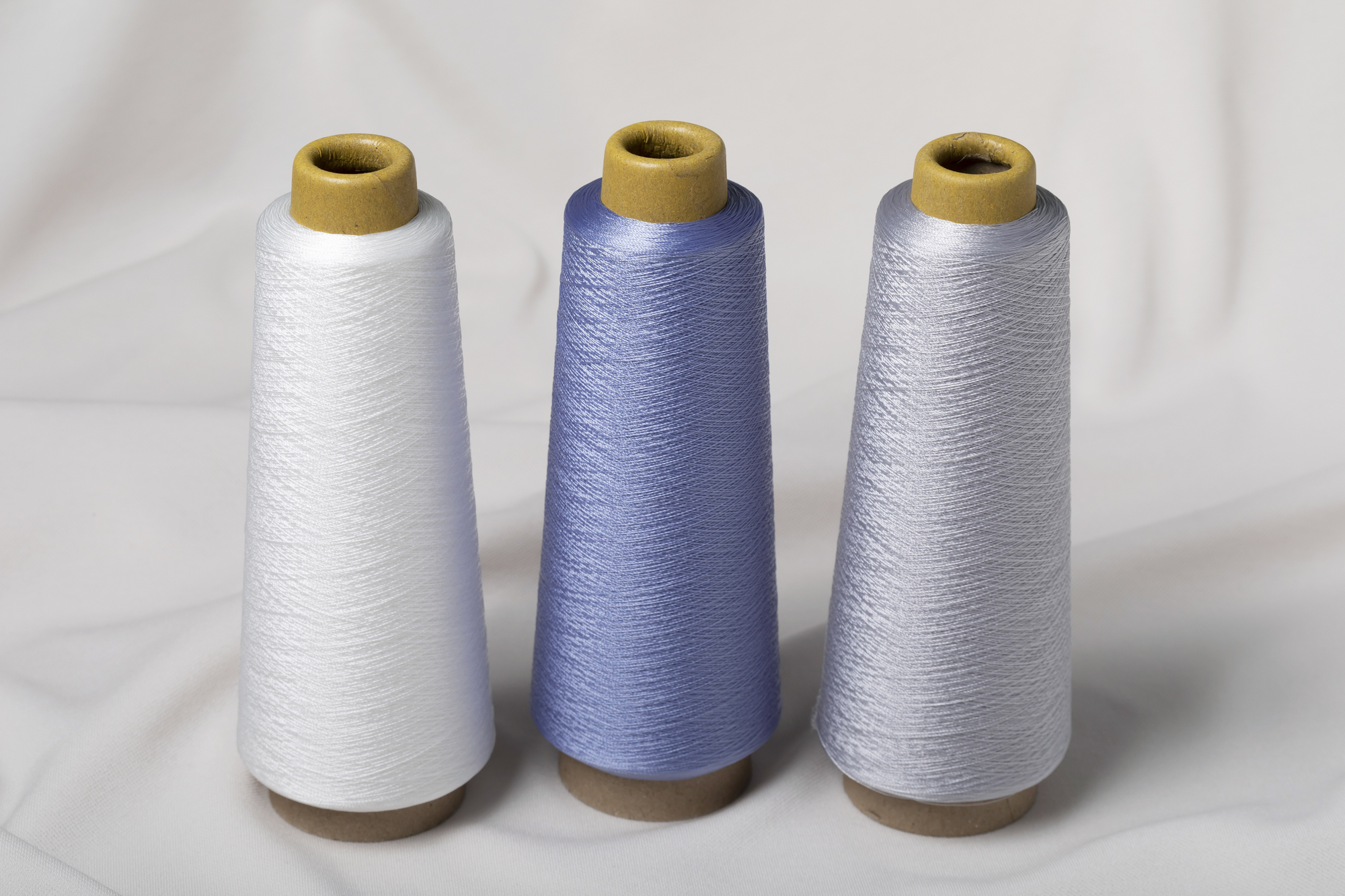
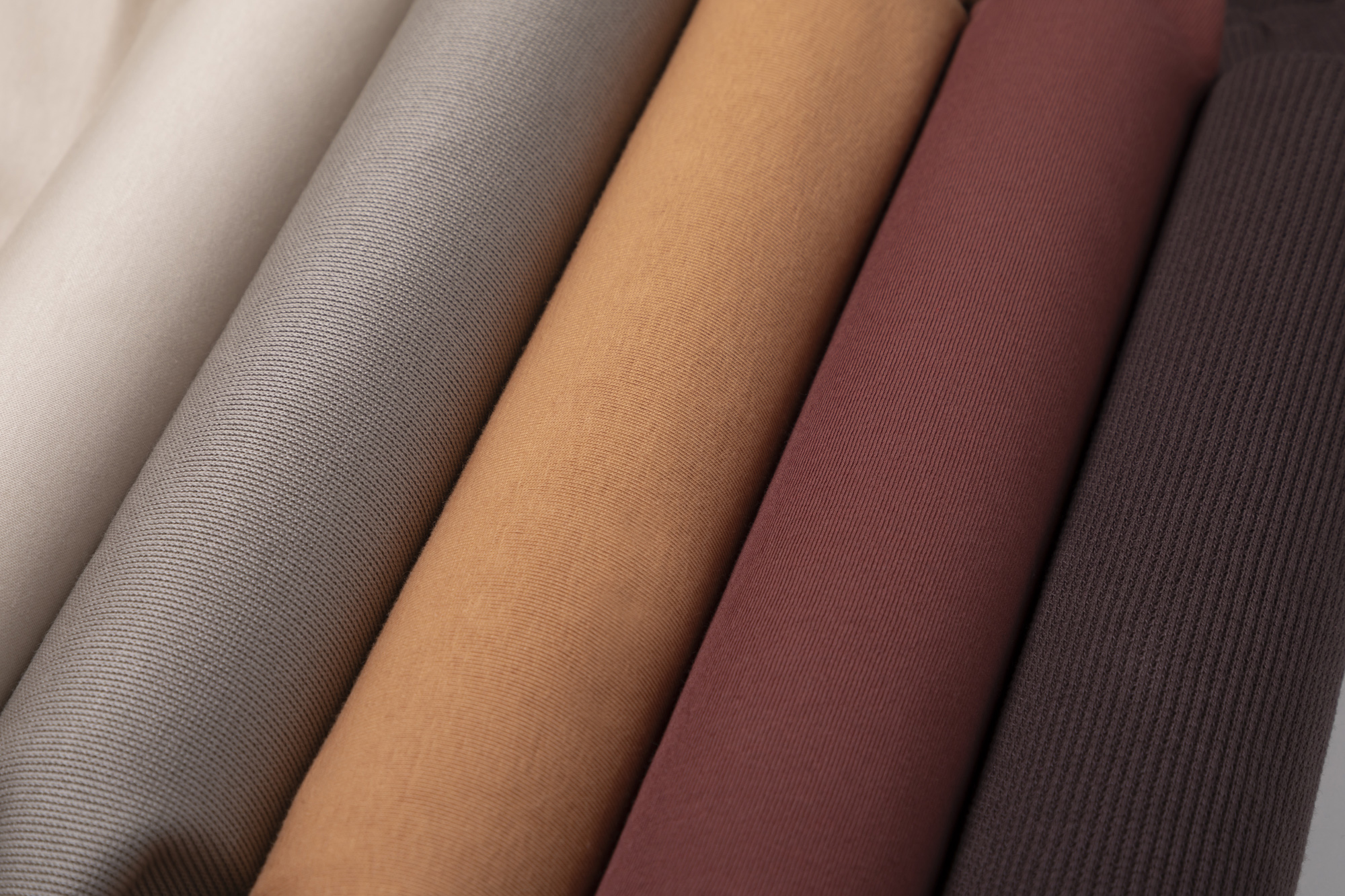
We have been developing polylactic acid (PLA) with the firm conviction that it is one of the few resins among biodegradable plastics that can be used for fibers.
Biodegradable plastic polylactic acid (PLA) has a simpler chemical structure than ordinary plastic, but this poses some challenges such as lack of strength, low thermal resistance and high production costs. In order to resolve these issues, HighChem has developed HIGHLACT® made from a next-generation PLA material by means of CHEMTEX, a fusion of CHEMICAL (strength in the chemical field that HighChem has cultivated over the years) and TEXTILE (Japan's outstanding traditional textile and dyeing technologies).
Used for injection molding
Polylactic acid (PLA) can be used for lunchboxes, food packaging containers for fruits and vegetables, precision parts, and compound raw materials.
*Conforming to Public Notification No. 370 of the Ministry of Health and Welfare under the Food Sanitation Act
Used for extrusion molding
Polylactic acid (PLA) can be used for films and sheets.

























